
Introduction
In the realm of gold mining and extraction, the all-slime cyanidation carbon-in-pulp (CIP) process has emerged as a pivotal technique. This process is particularly effective for treating gold ores with high clay content and fine particle size. In China, with its rich gold resources and a growing demand for gold, the all-slime cyanidation CIP process has found widespread application, playing a significant role in the domestic gold mining industry.
Principles of All-Slime Cyanidation Carbon-in-Pulp Process
The all-slime cyanidation CIP process is a combination of two key steps: Cyanidation leaching and carbon-in-pulp adsorption.
Cyanidation Leaching
Cyanidation leaching is the core of the process. Gold ores, after being crushed, ground, and pulped, are mixed with a cyanide solution. Under suitable conditions of pH, temperature, and oxygen supply, gold in the ore reacts with cyanide ions to form soluble gold cyanide complexes. The chemical reaction can be simply expressed as:
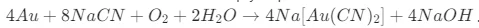
This reaction allows gold to be dissolved from the ore matrix into the solution, separating it from the gangue minerals.
Carbon-in-Pulp Adsorption
Once gold is dissolved in the cyanide solution, granular activated carbon is added directly to the leaching pulp. The activated carbon has a strong adsorption capacity for gold cyanide complexes. Through physical and chemical adsorption mechanisms, gold is adsorbed onto the surface of the activated carbon, effectively separating gold from the cyanide solution. This step eliminates the need for complex solid-liquid separation processes in traditional cyanidation methods, simplifying the overall extraction process.
Development History of All-Slime Cyanidation CIP Process in China
China's journey with the all-slime cyanidation CIP process dates back several decades.
Early Stages
In the mid-20th century, China's gold mining industry mainly relied on traditional Gold extraction methods, which had limitations in handling complex ores. As the demand for gold increased and more complex gold ore deposits were discovered, there was an urgent need to introduce advanced extraction technologies. The all-slime cyanidation CIP process was gradually introduced and studied. In the 1970s and 1980s, initial research and pilot-scale tests were carried out in some gold mines. For example, in some mines in Heilongjiang Province, attempts were made to apply this process to treat local gold ores, which laid the foundation for its future large-scale application.
Expansion and Maturity
In the following decades, with continuous technological innovation and improvement, the all-slime cyanidation CIP process began to be widely promoted and applied across the country. In the 1990s and 2000s, many gold mines in Henan, Shandong, Jilin, and other provinces built all-slime cyanidation CIP production lines. These mines continuously optimized the process parameters, improved equipment performance, and trained professional technical teams. As a result, the recovery rate of gold gradually increased, and production costs were effectively controlled. By the end of the 20th century, the all-slime cyanidation CIP process had become one of the mainstream gold extraction methods in China, accounting for a significant proportion of the country's gold production.
Applications of All-Slime Cyanidation CIP Process in Different Gold Mines in China
Shandong Province
Shandong is a major gold-producing province in China. Many large gold mines here have adopted the all-slime cyanidation CIP process. For example, the Jiaojia Gold Mine. The ore in the Jiaojia Gold Mine has certain characteristics of fine particle size and relatively high clay content. After adopting the all-slime cyanidation CIP process, the gold recovery rate has been significantly improved. Through strict control of the grinding fineness to ensure that the gold particles are fully exposed, adjusting the cyanide concentration and leaching time according to the ore properties, and optimizing the carbon adsorption process, the gold recovery rate of the Jiaojia Gold Mine has reached over 90%. This has not only increased the economic benefits of the mine but also improved the utilization rate of resources.
Henan Province
In Henan, the Lingbao area is rich in gold resources. The Yangzhaiyu Gold Mine in Lingbao is a typical example of applying the all-slime cyanidation CIP process. The mine has a large-scale all-slime cyanidation CIP production line. During the production process, in addition to following the standard process steps, it also innovatively added some pre-treatment processes for the ore. For example, through pre-oxidation treatment of some refractory ores, the difficulty of cyanidation leaching was reduced, and the overall efficiency of the all-slime cyanidation CIP process was improved. The success of the Yangzhaiyu Gold Mine has also driven the technological upgrading of other gold mines in the region.
Jilin Province
The Hushan Gold Mine in Jilin Province also makes full use of the all-slime cyanidation CIP process. Given the local cold climate and specific ore characteristics, the mine has made some adaptations to the process. For instance, in winter, special measures are taken to ensure the normal operation of the process in low-temperature environments, such as heating the slurry and optimizing the ventilation system in the leaching tank. By doing so, the mine has maintained stable production and a relatively high gold recovery rate, demonstrating the flexibility and adaptability of the all-slime cyanidation CIP process in different geographical and climatic conditions.
Advantages of All-Slime Cyanidation CIP Process in China
High Gold Recovery Rate
The all-slime cyanidation CIP process can achieve a high gold recovery rate, usually reaching over 85% in most gold mines in China. This is mainly because the direct addition of activated carbon in the pulp can effectively capture gold cyanide complexes, reducing the loss of gold in the leaching solution. For example, in the gold mines mentioned above, through continuous optimization of the process, the recovery rate has been further improved, which is much higher than some traditional gold extraction methods.
Simple Process Flow
Compared with some complex gold extraction processes, the all-slime cyanidation CIP process has a relatively simple flow. It omits some complex solid-liquid separation steps, such as filtration and washing in traditional cyanidation methods. This simplicity not only reduces the investment in equipment and infrastructure but also simplifies the operation and management of the production line, making it easier to control the production process and reduce the probability of process failures.
Adaptability to Different Ores
The process shows good adaptability to various types of gold ores, especially those with high clay content and fine particle size. Whether it is oxidized gold ore, sulfide gold ore, or some complex multi-metal associated gold ores, the all-slime cyanidation CIP process can be adjusted and optimized according to the ore properties to achieve better extraction results. This adaptability has enabled China to effectively utilize a wide range of gold ore resources.
Challenges and Solutions in the Application of All-Slime Cyanidation CIP Process in China
Environmental Concerns
One of the major challenges of the all-slime cyanidation CIP process is the use of cyanide, which is highly toxic. Although China has strict regulations and management measures for the use and disposal of cyanide, there are still potential environmental risks. In response, Chinese gold mines have been strengthening environmental protection measures. For example, they have built advanced cyanide wastewater treatment systems to ensure that the cyanide content in the discharged wastewater meets the national standards. Some mines are also actively researching and applying alternative leaching agents to reduce or replace the use of cyanide, such as the development and trial application of thiosulfate and some bio-leaching methods.
Ore Refractoriness
Some gold ores in China are refractory, which means that the gold in the ore is difficult to be leached by cyanide. This can reduce the gold recovery rate and increase production costs. To address this issue, gold mines often adopt pre-treatment methods. Physical pre-treatment methods include fine grinding, roasting, and high-pressure oxidation. Chemical pre-treatment methods such as bio-oxidation are also being gradually promoted. These pre-treatment methods can break the structure of refractory minerals, expose the gold particles, and improve the effectiveness of cyanidation leaching.
Future Prospects of All-Slime Cyanidation CIP Process in China
Technological Innovation
In the future, continuous technological innovation will be the key to the development of the all-slime cyanidation CIP process in China. Research and development efforts will focus on further improving the gold recovery rate, reducing production costs, and enhancing environmental friendliness. For example, the development of more efficient activated carbon with higher adsorption capacity and selectivity for gold will be an important direction. In addition, the application of intelligent control systems in the process to achieve more accurate process parameter adjustment and real-time monitoring of production will also be actively explored.
Expansion of Application Scope
With the continuous discovery of new gold ore deposits and the increasing demand for gold, the all-slime cyanidation CIP process is expected to be applied in more gold mines in China. At the same time, it may also be extended to the treatment of some low-grade gold ores and gold-containing industrial waste, further expanding the scope of resource utilization and contributing to the sustainable development of the gold mining industry.
Conclusion
The all-slime cyanidation carbon-in-pulp process has played an important role in China's gold mining industry. Through continuous development and improvement over the years, it has shown significant advantages in gold extraction. Although facing some challenges, with the joint efforts of the industry in technological innovation and environmental protection, the all-slime cyanidation CIP process is expected to continue to develop and contribute more to China's gold production and resource utilization in the future.
- Random Content
- Hot content
- Hot review content
- Sodium Peroxide
- Barium carbonate 99% powder
- Cobalt Sulphate Heptahydrate
- Phosphoric Acid 85% (Food grade)
- Isobutyl vinyl ether 98% high purity certified Professional producer
- Fuel Additive Octane Value Booster Ferrocene
- Sodium Dimethyldithiocarbamate 95% solid, 40% liquid
- 1Discounted Sodium Cyanide (CAS: 143-33-9) for Mining - High Quality & Competitive Pricing
- 2Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 3China's New Regulations on Sodium Cyanide Exports and Guidance for International Buyers
- 4International Cyanide(Sodium cyanide) Management Code - Gold Mine Acceptance Standards
- 5China factory Sulfuric Acid 98%
- 6Anhydrous Oxalic acid 99.6% Industrial Grade
- 7Soda Ash Dense / Light 99.2% Sodium Carbonate Washing Soda
- 1Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 2High Purity · Stable Performance · Higher Recovery — sodium cyanide for modern gold leaching
- 3Sodium Cyanide 98%+ CAS 143-33-9
- 4Sodium Hydroxide,Caustic Soda Flakes,Caustic Soda Pearls 96%-99%
- 5Nutritional Supplements Food Addictive Sarcosine 99% min
- 6Sodium Cyanide Import Regulations & Compliance – Ensuring Safe and Compliant Importation in Peru
- 7United Chemical's Research Team Demonstrates Authority Through Data-Driven Insights













Online message consultation
Add comment: