
Sodium cyanide, with the chemical formula NaCN, is a white, water - soluble, and highly toxic compound. Despite its notorious reputation due to its toxicity, it plays a crucial role in the Pharmaceutical Industry as an important chemical reagent in various synthetic processes.
1. Synthesis of Intermediates
1.1 Cyanohydrin Synthesis
One of the significant applications of Sodium Cyanide in pharmaceutical synthesis is in the formation of cyanohydrins. When an aldehyde or a ketone reacts with sodium cyanide in the presence of an acid catalyst (usually a weak acid), a cyanohydrin is produced. The reaction mechanism involves the nucleophilic addition of the cyanide ion (CN- ) to the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde or ketone. For example, in the synthesis of mandelonitrile, benzaldehyde reacts with Sodium cyanide. This reaction is represented as follows:
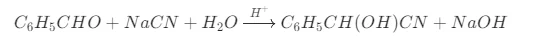
Mandelonitrile and other cyanohydrins are important intermediates in the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals. They can be further transformed into compounds with diverse biological activities, such as alpha - hydroxy acids and alpha - amino acids, which are integral parts of many drugs.
1.2 Nitrile Synthesis
Sodium cyanide is also widely used to synthesize nitriles. In an SN2 (substitution nucleophilic bimolecular) reaction, alkyl halides react with sodium cyanide to form nitriles. For instance, when bromoethane reacts with sodium cyanide, propionitrile is formed:

Nitriles are versatile building blocks in pharmaceutical chemistry. They can be hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids, reduced to amines, or further reacted to form heterocyclic compounds. Many drugs contain nitrile functional groups, which contribute to their pharmacological properties, such as in some antifungal and antibacterial agents.
2. Production of Specific Pharmaceuticals
2.1 Cyanocobalamin (Vitamin B12) Synthesis
Cyanocobalamin, commonly known as vitamin B12. is an essential vitamin for human health. The synthesis of cyanocobalamin involves the use of sodium cyanide. In the final step of some synthetic routes, a cobalt - containing intermediate is reacted with sodium cyanide to introduce the cyanide group, which is characteristic of cyanocobalamin. The cyanide group in cyanocobalamin is relatively stable under physiological conditions and plays a role in the vitamin's biological activity. Vitamin B12 is crucial for DNA synthesis, nerve function, and the production of red blood cells, and its synthetic production using sodium cyanide helps meet the demand for dietary supplements and pharmaceutical formulations.
2.2 Synthesis of Some Anti - cancer Drugs
In the development of certain anti - cancer drugs, sodium cyanide is used in the synthesis of key intermediates. For example, in the synthesis of some indole - based anti - cancer compounds, sodium cyanide is used in a series of reactions to construct the molecular framework. The nitrile groups introduced by sodium cyanide can be further modified to enhance the drug's affinity for cancer cells, inhibit specific enzymes involved in cancer cell growth, or disrupt the cancer cell's metabolic pathways.
3. Challenges and Precautions in Using Sodium Cyanide
The use of sodium cyanide in the pharmaceutical industry comes with significant challenges due to its extreme toxicity. Stringent safety measures are required in its handling, storage, and use. Specialized equipment and trained personnel are essential to prevent any leakage or exposure. In the manufacturing process, proper ventilation systems are installed to avoid the inhalation of any cyanide - containing fumes. Additionally, waste management is a critical aspect. Any waste containing sodium cyanide or its reaction products must be treated carefully to ensure environmental safety. Usually, oxidation methods are employed to convert the highly toxic cyanide compounds into less harmful substances before disposal.
4. Future Perspectives
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, the search for more efficient and safer synthetic methods is ongoing. While sodium cyanide remains an important reagent in current pharmaceutical synthesis, efforts are being made to develop alternative routes that either reduce or eliminate the use of this highly toxic compound. However, in the near future, due to the unique reactivity of sodium cyanide in certain synthetic pathways, it is likely to continue to play a role in the production of some pharmaceuticals. Research may focus on developing more controlled reaction conditions to minimize the risks associated with its use and on finding safer analogs or alternative synthetic strategies that can achieve the same pharmaceutical products with reduced toxicity concerns.
In conclusion, sodium cyanide, despite its toxicity, has made significant contributions to the pharmaceutical industry in the synthesis of various important drugs and intermediates. Its proper and safe use, along with continuous efforts to find alternatives, will be crucial for the sustainable development of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
- Random Content
- Hot content
- Hot review content
- Industrial grade sodium hexametaphosphate 68% SHMP
- Company product introduction
- industry Electric Detonator
- Potassium Permanganate – Industrial Grade
- Industrial Acetic Acid 99.5% Colorless Liquid Glacial acetic acid
- Food Grade Heavy Light Precipitated Calcium Carbonate Powder Granular 99%
- Isobutyl vinyl ether 98% high purity certified Professional producer
- 1Discounted Sodium Cyanide (CAS: 143-33-9) for Mining - High Quality & Competitive Pricing
- 2Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 3China's New Regulations on Sodium Cyanide Exports and Guidance for International Buyers
- 4International Cyanide(Sodium cyanide) Management Code - Gold Mine Acceptance Standards
- 5China factory Sulfuric Acid 98%
- 6Anhydrous Oxalic acid 99.6% Industrial Grade
- 7Oxalic acid for mining 99.6%
- 1Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 2High Purity · Stable Performance · Higher Recovery — sodium cyanide for modern gold leaching
- 3Sodium Cyanide 98%+ CAS 143-33-9
- 4Sodium Hydroxide,Caustic Soda Flakes,Caustic Soda Pearls 96%-99%
- 5Nutritional Supplements Food Addictive Sarcosine 99% min
- 6Sodium Cyanide Import Regulations & Compliance – Ensuring Safe and Compliant Importation in Peru
- 7United Chemical's Research Team Demonstrates Authority Through Data-Driven Insights













Online message consultation
Add comment: