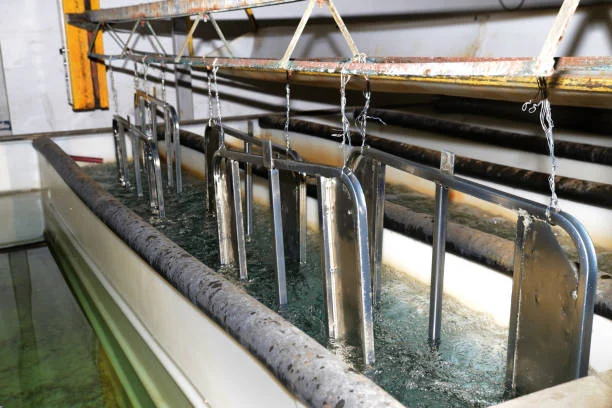

Introduction
Electroplating is a widely used industrial process for depositing a thin layer of metal onto a substrate through electrochemical means. This process not only enhances the aesthetic appearance of the substrate but also improves its corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and other mechanical properties. Sodium cyanide, a highly reactive and toxic compound, plays an indispensable role in many Electroplating applications. This article delves into the specific functions and significance of Sodium cyanide in electroplating processes.
Complexing Agent Function
One of the primary roles of Sodium Cyanide (NaCN) in electroplating is acting as a complexing agent. In electroplating baths, metal ions from the plating solution need to be transported to the surface of the substrate for deposition. However, free metal ions in solution can lead to rapid and uneven deposition, resulting in poor - quality coatings. Sodium cyanide reacts with metal ions, such as copper, zinc, gold, and silver, to form stable metal - cyanide complexes.
For example, in a copper - electroplating bath, sodium cyanide combines with copper ions. The resulting copper - cyanide complex is much more stable in the solution compared to free copper ions. This complexation offers several benefits. Firstly, it reduces the activity of the metal ions in the solution, which in turn decreases the rate of deposition. A slower deposition rate is crucial for achieving a smooth, uniform, and adherent metal coating. If the deposition rate is too fast, the metal atoms do not have enough time to arrange themselves properly on the substrate surface, leading to a rough and porous coating.
Secondly, the metal - cyanide complexes are more soluble in the plating solution. This enhanced solubility ensures a continuous supply of metal ions to the cathode (the substrate being plated) during the electroplating process. In gold electroplating, the formation of the gold - cyanide complex allows gold to remain in solution and be deposited evenly on the substrate.
Adjusting Cathode Polarization
Sodium cyanide also significantly affects the cathode polarization in electroplating. Cathode polarization refers to the change in the potential of the cathode during the electroplating process due to the electrochemical reactions occurring at its surface. A proper level of cathode polarization is essential for obtaining high - quality deposits.
When sodium cyanide is present in the electroplating bath, it increases the cathode polarization. The cyanide ions adsorb on the surface of the cathode, creating a barrier that restricts the movement of metal ions towards the cathode. This increases the overpotential required for the metal deposition reaction to occur. As a result, the metal ions are deposited more slowly and in a more controlled manner.
In a zinc - electroplating bath, for instance, the presence of sodium cyanide as a complexing agent and its subsequent effect on cathode polarization lead to a finer - grained zinc deposit. The increased cathode polarization forces the zinc ions to deposit at a slower rate, allowing them to arrange themselves in a more ordered manner on the substrate surface, thus improving the quality of the zinc coating.
Promoting Anode Dissolution
In addition to its effects on the cathode, sodium cyanide also plays a role in promoting the dissolution of the anode in the electroplating cell. The anode is the source of metal ions in the electroplating process. For a continuous and efficient electroplating operation, the anode must dissolve at a steady rate to replenish the metal ions consumed at the cathode.
Sodium cyanide helps in this process by forming soluble metal - cyanide complexes at the anode surface. In a copper - electroplating setup, the copper anode dissolves when it reacts with sodium cyanide. The formation of the copper - cyanide complex at the anode surface facilitates the dissolution of copper. This is because the complexation reaction removes the copper ions from the anode surface as soon as they are formed, preventing the build - up of a passive layer on the anode. A passive layer can inhibit further anode dissolution and disrupt the electroplating process. By promoting anode dissolution, sodium cyanide ensures a consistent supply of metal ions to the electroplating bath, maintaining a stable plating process.
Applications in Different Electroplating Processes
Gold and Silver Electroplating
Sodium cyanide is extensively used in gold and silver electroplating. In the jewelry industry, gold - plated items are produced by electroplating a thin layer of gold onto a base metal like copper or silver. The use of sodium cyanide in the gold - plating bath helps in obtaining a bright, smooth, and adherent gold coating. The gold - cyanide complex formed in the presence of sodium cyanide allows for precise control over the deposition of gold, ensuring that the plated layer has the desired thickness and quality.
Similarly, in silver electroplating, sodium cyanide forms silver - cyanide complexes, which are crucial for achieving high - quality silver coatings. The use of sodium cyanide in these precious metal electroplating processes has been the industry standard for a long time due to the excellent results it produces in terms of coating quality.
Copper Electroplating
In copper electroplating, sodium cyanide is used to form copper - cyanide complexes. This is particularly important in applications where a smooth and highly adherent copper coating is required, such as in the electronics industry for plating printed circuit boards. The copper - cyanide complexes formed in the presence of sodium cyanide enable the deposition of a uniform copper layer, which is essential for ensuring proper electrical conductivity and reliability of the circuit boards.
Zinc Electroplating
Although efforts are being made to develop non - cyanide zinc - electroplating processes, sodium cyanide is still used in some traditional zinc - electroplating baths. In zinc electroplating, sodium cyanide helps in complexing zinc ions to form zinc - cyanide complexes. This complexation not only affects the deposition rate and quality of the zinc coating but also helps in controlling the composition of the coating. For example, in zinc - alloy electroplating (such as zinc - nickel or zinc - iron alloys), the presence of sodium cyanide can influence the ratio of different metals in the alloy deposit, which in turn affects the properties of the final coating, such as corrosion resistance and hardness.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
While sodium cyanide is highly effective in electroplating processes, it is important to note that it is a extremely toxic compound. Even a small amount of sodium cyanide can be lethal if ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin. Therefore, strict Safety measures must be in place in electroplating facilities that use sodium cyanide. Workers handling sodium cyanide must be properly trained and equipped with personal protective equipment, including gloves, goggles, and respiratory protection.
In addition, the disposal of waste materials containing sodium cyanide or its reaction products must be carefully managed to prevent environmental contamination. Cyanide - containing wastewaters from electroplating processes need to be treated to remove or detoxify the cyanide before being discharged. Common treatment methods include chemical oxidation (using oxidizing agents such as chlorine or hydrogen peroxide) to convert the cyanide to less toxic compounds.
Conclusion
Sodium cyanide plays a multifaceted and crucial role in electroplating processes. As a complexing agent, it forms stable metal - cyanide complexes that improve the solubility and transport of metal ions in the plating bath, leading to more uniform and adherent metal coatings. It also adjusts cathode polarization and promotes anode dissolution, both of which are essential for a smooth and efficient electroplating operation. Despite its toxicity, when used with proper safety and environmental precautions, sodium cyanide continues to be an important component in many electroplating applications, especially in the deposition of precious metals and in achieving high - quality coatings for various industrial and decorative purposes. However, ongoing research is also focused on developing alternative, more environmentally friendly electroplating processes to reduce the reliance on this toxic compound.
- Random Content
- Hot content
- Hot review content
- Toxicity Assessment of Sodium Cyanide and Relevant Hazard Prevention Measures
- Lead Chloride/ Lead (II) Chloride 98%
- Isobutyl vinyl ether 98% high purity certified Professional producer
- Benzonitrile
- 99% Animal Feed Additive DL Methionine
- Magnesium Sulfate
- Sodium Dimethyldithiocarbamate 95% solid, 40% liquid
- 1Discounted Sodium Cyanide (CAS: 143-33-9) for Mining - High Quality & Competitive Pricing
- 2Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 3Sodium Cyanide 98%+ CAS 143-33-9
- 4Anhydrous Oxalic acid 99.6% Industrial Grade
- 5Oxalic acid for mining 99.6%
- 6Soda Ash Dense / Light 99.2% Sodium Carbonate Washing Soda
- 7Reagent Grade/Industrial Grade Hydrochloric Acid min.31%
- 1Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 2High Quality 99% Purity of Cyanuric chloride ISO 9001:2005 REACH Verified Producer
- 3 High-Quality Sodium Cyanide for Leaching
- 4Powdery emulsion explosive
- 5Industry Grade Electron grade 98% Sulfuric Acid H2SO4 Sulphuric Acid Battery Acid Industrial Sulfuric Acid
- 6Colloidal emulsion explosive
- 7sodium hydrosulfide 70% flakes used Mining Industry










Online message consultation
Add comment: