Sodium cyanide is a highly toxic compound that poses significant health risks, particularly in industrial settings or during accidental exposure. In the event of Sodium cyanide poisoning, immediate and effective First aid measures are crucial for survival. This article outlines essential first aid steps that can be taken to assist individuals affected by Sodium cyanide poisoning, emphasizing the importance of prompt action and safety precautions for both the victim and the rescuer.
Recognizing Symptoms of Sodium Cyanide Poisoning
Before delving into first aid measures, it is vital to recognize the symptoms of Sodium Cyanide poisoning. Symptoms may include:
Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
Dizziness or lightheadedness
Headache
Nausea and vomiting
Confusion or altered mental state
Seizures
Loss of consciousness
If you suspect someone has been exposed to sodium cyanide, it is imperative to act quickly.
Immediate First Aid Steps
Ensure Safety First: Before approaching the victim, ensure your own safety. If the poisoning occurred in a confined space or an area with potential cyanide gas exposure, do not enter without proper protective equipment, such as an oxygen supply gas mask. If necessary, call emergency services to handle the situation.
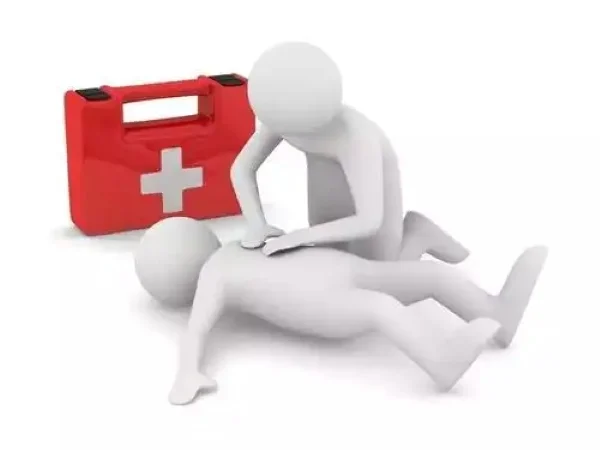
Assess Breathing and Circulation: If the victim is unresponsive, check for breathing and pulse. If the patient has stopped breathing or their heart has ceased beating, initiate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) immediately. Avoid mouth-to-mouth resuscitation to prevent the risk of poisoning the rescuer. Instead, perform chest compressions and artificial respiration by squeezing the chest or stretching the upper limbs.
Move to Fresh Air: If the victim has been exposed to sodium cyanide gas, it is critical to move them to an area with fresh air as quickly as possible. This step is vital to reduce further exposure to the toxic substance.
Position the Victim: Once in a safe location, lay the victim flat on their back and keep them warm. This position helps maintain blood flow to vital organs.
Remove Contaminated Clothing: If the victim's clothing is contaminated with sodium cyanide, remove it immediately to prevent further skin absorption of the toxin.
Decontamination: If the skin is contaminated, rinse the affected area thoroughly with a 1:2000 potassium permanganate solution or warm water. This step is essential to minimize the absorption of cyanide through the skin.
Induce Vomiting (if conscious): If the victim is conscious and has ingested sodium cyanide, induce vomiting and perform gastric lavage immediately. However, ensure that the airway remains open to prevent suffocation due to vomiting. Call for help from emergency services while performing these actions.
Advanced First Aid Measures
In addition to the immediate first aid steps, there are advanced measures that can be taken to counteract the effects of sodium cyanide poisoning:
Nitrite Sodium Thiosulfate Therapy: This treatment involves the administration of sodium nitrite and isoamyl nitrite. These compounds work by generating methemoglobin, which can bind to cyanide ions, effectively displacing them from cytochrome oxidase. This process restores the activity of cytochrome oxidase, allowing the body to utilize oxygen more effectively.
Gastric Lavage: For patients who regain consciousness, gastric lavage can be performed using a 1:5000 potassium permanganate solution, hydrogen peroxide solution, or a 2% baking soda solution. Administer approximately 500 mL of the solution until the patient vomits. This procedure helps to remove any remaining cyanide from the stomach.
Oxygen Administration: If the victim is experiencing difficulty breathing, provide supplemental oxygen. This step is crucial for patients who are hypoxic due to cyanide exposure.
Continuous Monitoring: Throughout the first aid process, continuously monitor the victim's vital signs, including breathing, pulse, and level of consciousness. Be prepared to perform CPR again if necessary.
Seek Medical Attention: Regardless of the initial response, it is essential to seek professional medical treatment as soon as possible. Sodium cyanide poisoning can have severe and lasting effects, and medical professionals will have access to advanced treatments and antidotes.
Conclusion
Sodium cyanide poisoning is a life-threatening emergency that requires immediate action. Understanding the first aid measures outlined in this guide can make a significant difference in the outcome for a victim of cyanide exposure. Always prioritize safety for both the rescuer and the victim, and do not hesitate to call for professional medical assistance. By acting quickly and effectively, you can help save a life in the event of sodium cyanide poisoning.
- Random Content
- Hot content
- Hot review content
- QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMCERTIFICATE
- Booster(Detonating insensitive explosives)
- Thiourea 99% high activity Professional Producer
- Citric acid-Food Grade
- Dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid
- Phosphoric Acid 85% (Food grade)
- Gold Ore Dressing Agent Safe Gold Extracting Agent Replace Sodium Cyanide
- 1Discounted Sodium Cyanide (CAS: 143-33-9) for Mining - High Quality & Competitive Pricing
- 2Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 3Sodium Cyanide 98%+ CAS 143-33-9
- 4China's New Regulations on Sodium Cyanide Exports and Guidance for International Buyers
- 5Anhydrous Oxalic acid 99.6% Industrial Grade
- 6Oxalic acid for mining 99.6%
- 7Reagent Grade/Industrial Grade Hydrochloric Acid min.31%
- 1Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 2High Quality 99% Purity of Cyanuric chloride ISO 9001:2005 REACH Verified Producer
- 3 High-Quality Sodium Cyanide for Leaching
- 4Powdery emulsion explosive
- 5Industry Grade Electron grade 98% Sulfuric Acid H2SO4 Sulphuric Acid Battery Acid Industrial Sulfuric Acid
- 6Colloidal emulsion explosive
- 7sodium hydrosulfide 70% flakes used Mining Industry











Comments
Add comment: