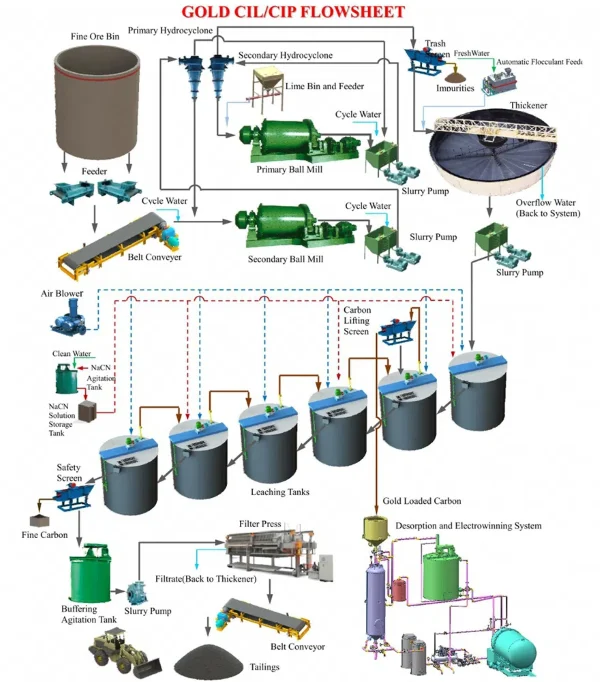
Gold cyanidation is a method of extracting gold using cyanide as a leaching agent. Due to its mature technical level, high leaching rate, and strong applicability to ores, the cyanidation method remains one of the main gold extraction methods at present. In the Gold cyanidation process, every step must be controlled to ensure good economic benefits while reducing equipment weight and investment.
1. Aeration and Cyanide Addition
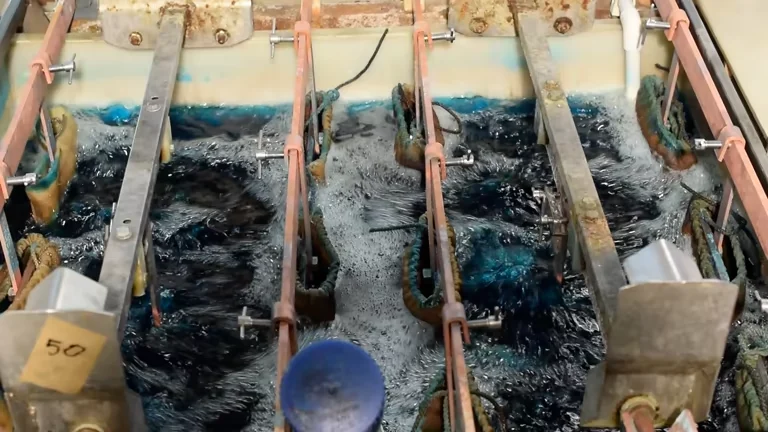
After grinding, cyanide is added to the pulp to dissolve gold and form metal complexes. The reaction formula is as follows: 4Au + 8NaCN + O2 + 2H2O → 4NaAu(CN)2 + 4NaOH. As can be seen from the above formula, oxygen is required in the process of leaching gold. Therefore, in industrial production, the leaching tank needs to be aerated. The aeration pressure is generally about 1 kg, and the aeration volume per minute for each cubic meter of slurry is greater than 0.002 m³.
2. Adding Protective Alkali
To ensure the concentration of cyanide in the pulp, avoid environmental pollution, and prevent the generation of toxic hydrogen cyanide (HCN) gas, alkali must be added to the leaching tank to maintain a high pH value of the pulp. Lime or lime milk is often used in industrial production, and sometimes NaOH is added for supplementary adjustment.
3. Maintaining Slurry Suspension
The gold cyanidation process has certain requirements for the performance of the leaching agitation tank. With low power consumption, the particles of monomer-separated or exposed surface gold in the pulp should not deposit in the tank. The pulp, cyanide, lime, and air should be fully mixed in the tank to reach a suspended state. The slurry concentration in each part of the tank should be consistent, and there should be no stratification along the depth direction of the tank, and the particle size distribution should be uniform.
4. Maintaining Appropriate Slurry Concentration
When the density of gold ore is 2.65 - 2.8. the general leaching pulp concentration is 40 - 45%. When the density of flotation concentrate is 3 - 3.5. the general leaching concentration is 30 - 40%. Generally, materials with a fineness less than 200 mesh account for 80 - 95%.
5. Reducing Wear and Noise of Moving Parts
To reduce the wear of the agitator and increase its service life, most impellers in industrial production are rubber-lined. The selection of the transmission device should be meticulous to ensure high transmission efficiency and low noise.
6. Reducing Carbon Wear
The carbon-in-pulp method adds carbon to the adsorption tank to adsorb gold. If the agitation force of the leaching tank is too strong, the carbon will be ground and lost. If the agitation force is weak, sediment will be generated. Therefore, while maintaining the pulp in a suspended state, on the one hand, it is necessary to select high-hardness carbon for production, and on the other hand, it is necessary to reduce the rotation speed of the impeller to reduce the loss of pulp, carbon, and the input power of the agitation adsorption tank.
7. Determining Appropriate Capacity
Currently, the processing capacity of common gold cyanidation plants ranges from several tens of tons to tens of thousands of tons per day. The larger the production capacity, the larger the plant area, and the larger the equipment specifications and investment. Each mine owner must determine an appropriate processing plant capacity according to the actual situation.
8. Reducing Equipment Weight and Investment
When selecting the leaching tank, on the one hand, the leaching process is required to be efficient and energy-saving, and at the same time, the transmission device is required to have a small footprint and light weight. When the capacity, pulp concentration, and leaching time are determined, the number of leaching tanks can be determined. However, the specifications of the leaching tanks should be suitable for the plant capacity. When building a 500t/d gold cyanidation plant, if a φ3.5X3.5m leaching tank is used, the required equipment needs to be increased, increasing the investment. Therefore, only with light equipment and an appropriate capacity can the construction investment of the enterprise be reduced.
- Random Content
- Hot content
- Hot review content
- Toxicity Assessment of Sodium Cyanide and Relevant Hazard Prevention Measures
- Powdery emulsion explosive
- Plastic Shock Tube(VOD≧1600m/s)
- Toluene
- Antimonium Tartrate Potassium
- Hydrogen Peroxide
- Gold Ore Dressing Agent Safe Gold Extracting Agent Replace Sodium Cyanide
- 1Discounted Sodium Cyanide (CAS: 143-33-9) for Mining - High Quality & Competitive Pricing
- 2Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 3Sodium Cyanide 98%+ CAS 143-33-9
- 4Anhydrous Oxalic acid 99.6% Industrial Grade
- 5Oxalic acid for mining 99.6%
- 6Soda Ash Dense / Light 99.2% Sodium Carbonate Washing Soda
- 7Reagent Grade/Industrial Grade Hydrochloric Acid min.31%
- 1Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 2High Quality 99% Purity of Cyanuric chloride ISO 9001:2005 REACH Verified Producer
- 3 High-Quality Sodium Cyanide for Leaching
- 4Powdery emulsion explosive
- 5Industry Grade Electron grade 98% Sulfuric Acid H2SO4 Sulphuric Acid Battery Acid Industrial Sulfuric Acid
- 6Colloidal emulsion explosive
- 7sodium hydrosulfide 70% flakes used Mining Industry












Online message consultation
Add comment: