
In the complex and resource - intensive process of Gold Mining, Sodium Cyanide plays a crucial and often misunderstood role. This article aims to comprehensively explain how this chemical compound contributes to the extraction of gold from its ores.
The Principle of Sodium Cyanide in Gold Extraction
Gold, in its natural state, often exists in low - grade ores, making it difficult to separate from the surrounding rock and minerals. Sodium cyanide (NaCN) reacts with gold in a process known as Cyanidation. The cyanide ions in sodium cyanide form a stable complex with gold ions. The chemical reaction can be simply represented as:
4Au + 8NaCN+O_{2}+2H_{2}O\rightarrow4Na[Au(CN)_{2}]+4NaOH
This reaction selectively dissolves gold from the ore, separating it from the gangue (the unwanted minerals and rock). The resulting gold - cyanide complex, [Au(CN)_{2}]^{-}, is soluble in water, which is the key to its separation from the rest of the ore components.
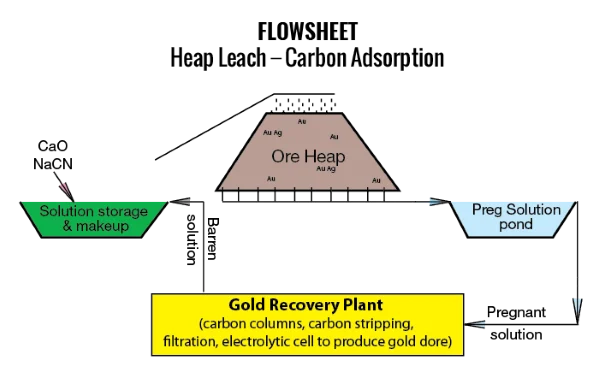
The Process of Using Sodium Cyanide in Gold Mining
Ore Preparation: First, the mined gold - bearing ore is crushed and ground into a fine powder. This increases the surface area of the ore, allowing for more efficient contact between the gold particles and the Sodium cyanide solution.
Leaching: The powdered ore is then placed in large tanks or heaps, and a dilute solution of sodium cyanide is sprayed or percolated through it. The cyanide solution slowly dissolves the gold over a period that can range from several hours to several days, depending on the nature of the ore.
Recovery of Gold - Cyanide Complex: After the Leaching process, the solution containing the gold - cyanide complex is separated from the solid residue (gangue). This is usually done through methods such as filtration or sedimentation.
Gold Precipitation: To obtain pure gold from the gold - cyanide complex solution, a reducing agent, such as zinc dust, is added. The zinc displaces the gold in the complex, causing the gold to precipitate out as a solid. The chemical reaction is as follows:
2Na[Au(CN)_{2}]+Zn\rightarrow2Au + Na_{2}[Zn(CN)_{4}]
The precipitated gold is then further refined through processes like smelting to obtain high - purity gold bars.
Advantages of Using Sodium Cyanide in Gold Mining
High Efficiency: Cyanidation is one of the most efficient methods for extracting gold from low - grade ores. It can recover a significant proportion of the gold present in the ore, often reaching recovery rates of 80 - 95% in well - optimized operations.
Selectivity: Sodium cyanide shows a high degree of selectivity towards gold. It preferentially reacts with gold over many other common minerals found in gold ores, which helps in separating gold from a complex mixture of substances with relative ease.
Cost - Effectiveness: Compared to some alternative gold extraction methods, such as mercury amalgamation (which has significant environmental and health risks) or more complex and energy - intensive chemical processes, cyanidation using sodium cyanide is relatively cost - effective, especially for large - scale mining operations.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Despite its effectiveness, the use of sodium cyanide in gold mining is not without controversy. Sodium cyanide is highly toxic. Any leakage or improper handling of sodium cyanide solutions can pose a severe threat to the environment and human health. In case of a spill, cyanide can contaminate soil, water sources, and harm aquatic life. To mitigate these risks, mining companies implement strict safety protocols. These include double - lining of storage and leaching ponds, continuous monitoring of cyanide levels in waste streams, and the use of advanced treatment methods to detoxify cyanide - containing waste before disposal. Additionally, efforts are being made to develop alternative, more environmentally friendly gold extraction methods, but currently, cyanidation with sodium cyanide remains the dominant technique in the gold mining industry due to its efficiency and cost - effectiveness.
In conclusion, sodium cyanide is an essential tool in modern gold mining. Its ability to selectively dissolve gold from ores, combined with its relatively low cost and high efficiency, makes it indispensable in the extraction of this precious metal. However, the industry must continue to balance its use with strict environmental and safety measures to ensure sustainable gold mining practices.
- Random Content
- Hot content
- Hot review content
- Industry Grade Electron grade 98% Sulfuric Acid H2SO4 Sulphuric Acid Battery Acid Industrial Sulfuric Acid
- Sodium Metal, ≥99.7%
- Ferrous Sulfate Industrial Grade 90%
- Sodiumsulfite Technical Grade 96%-98%
- Toluene
- Food Grade Heavy Light Precipitated Calcium Carbonate Powder Granular 99%
- calcium chloride anhydrous for food
- 1Discounted Sodium Cyanide (CAS: 143-33-9) for Mining - High Quality & Competitive Pricing
- 2Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 3Sodium Cyanide 98%+ CAS 143-33-9
- 4China's New Regulations on Sodium Cyanide Exports and Guidance for International Buyers
- 5Anhydrous Oxalic acid 99.6% Industrial Grade
- 6Oxalic acid for mining 99.6%
- 7Reagent Grade/Industrial Grade Hydrochloric Acid min.31%
- 1Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 2High Quality 99% Purity of Cyanuric chloride ISO 9001:2005 REACH Verified Producer
- 3 High-Quality Sodium Cyanide for Leaching
- 4Powdery emulsion explosive
- 5Industry Grade Electron grade 98% Sulfuric Acid H2SO4 Sulphuric Acid Battery Acid Industrial Sulfuric Acid
- 6Colloidal emulsion explosive
- 7sodium hydrosulfide 70% flakes used Mining Industry











Online message consultation
Add comment: