
Sodium cyanide is a highly toxic chemical. Even minimal contact through skin wounds, inhalation, or ingestion can lead to fatal poisoning. However, it serves as a fundamental raw material in various industries, including mechanical engineering, the chemical industry, the pharmaceutical sector, and metallurgy. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the precautions that must be taken when transporting sodium cyanide.
Packaging
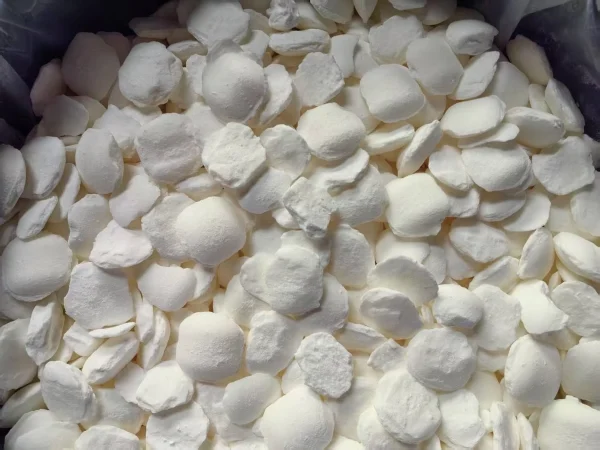
Both solid and liquid Sodium Cyanide should be packed in glass bottles placed inside wooden crates or in iron drums. This packaging method helps prevent leakage and potential exposure during transportation.
Storage
Storage Environment: Sodium cyanide should be stored in a dry and well - ventilated warehouse. It is advisable to have a dedicated warehouse for its storage.
Security Measures: The warehouse should be under the supervision of two - person, two - key management to enhance security and prevent unauthorized access.
Personal Protective Measures for Workers
Entry Precautions: Workers entering the warehouse must wear work uniforms, gas - mask respirators, and other appropriate protective equipment.
Post - work Procedures: After work, all protective gear should be removed. Workers should thoroughly wash their hands and faces with water. Additionally, they should soak their hands in a dilute sodium hypochlorite solution for disinfection before rinsing with water.
Behavioral Restrictions: Workers should avoid drinking tea or smoking during work breaks. Individuals with unhealed skin wounds should not come into contact with Sodium cyanide.
Transportation and Storage Restrictions
Avoiding Contamination: Sodium cyanide should never be stored or transported together with acids, chlorates, sodium nitrite, or food raw materials.
Moisture and Seal Integrity: It is crucial to prevent sodium cyanide from getting damp. All containers must be tightly sealed to prevent leakage and potential reactions.
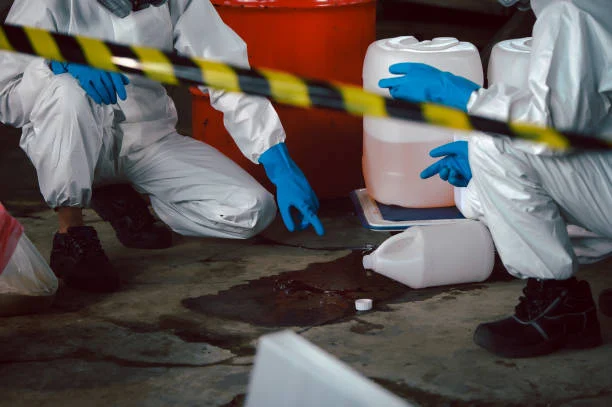
Handling of Spills
Immediate Response: In the event of a spill, responders must wear gas - mask respirators and gloves. The spilled material should be swept up and mixed with an excess of sodium hypochlorite solution. The mixture should be left for 24 hours to ensure complete decomposition of sodium cyanide. Afterward, it can be diluted and discharged into the wastewater treatment system.
Pollution Area Remediation: The contaminated area should be soaked with sodium hypochlorite solution for 24 hours. Subsequently, it should be thoroughly flushed with a large amount of water, and the rinse water should be directed into the wastewater system.
By strictly adhering to these precautions, we can minimize the risks associated with the transportation of sodium cyanide and ensure the safety of both workers and the environment.
- Random Content
- Hot content
- Hot review content
- Sodium Ethyl Xanthate 90% SEX
- Sodium Amyl Xanthate (SAX) 90%, Mining chemical, mining flotation reagent
- High-strength, High-precision Shock Tube Detonator
- Digital Electronic Detonator(Delay time 0~ 16000ms)
- 99.5% min Ammonium Chloride For Industrial Use
- Sodium Peroxide
- Hydrogen Peroxide
- 1Discounted Sodium Cyanide (CAS: 143-33-9) for Mining - High Quality & Competitive Pricing
- 2Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 3Sodium Cyanide 98%+ CAS 143-33-9
- 4China's New Regulations on Sodium Cyanide Exports and Guidance for International Buyers
- 5Anhydrous Oxalic acid 99.6% Industrial Grade
- 6Oxalic acid for mining 99.6%
- 7Reagent Grade/Industrial Grade Hydrochloric Acid min.31%
- 1Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 2High Quality 99% Purity of Cyanuric chloride ISO 9001:2005 REACH Verified Producer
- 3 High-Quality Sodium Cyanide for Leaching
- 4Powdery emulsion explosive
- 5Industry Grade Electron grade 98% Sulfuric Acid H2SO4 Sulphuric Acid Battery Acid Industrial Sulfuric Acid
- 6Colloidal emulsion explosive
- 7sodium hydrosulfide 70% flakes used Mining Industry











Online message consultation
Add comment: