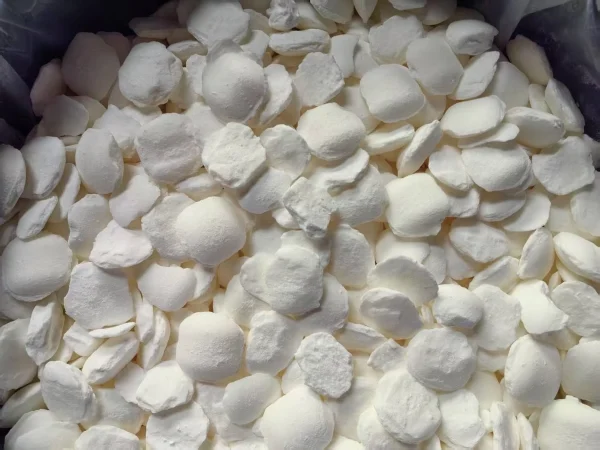

Sodium cyanide is a highly toxic chemical, and its handling demands strict adherence to safety protocols. All personnel who come into contact with Sodium cyanide must be thoroughly familiar with and comply with established safety procedures.
Health Hazards Associated with Sodium Cyanide
Inhalation of Sodium Cyanide dust can lead to immediate poisoning. Prolonged skin contact, especially in the presence of open wounds or abrasions, may cause irritation and potentially result in systemic poisoning. Additionally, sodium cyanide can cause severe eye burns.
One of the most dangerous aspects of sodium cyanide is its reaction with acids or weak bases. This reaction releases highly toxic and flammable Hydrogen cyanide (HCN) gas. Even from an aqueous solution of sodium cyanide, toxic levels of HCN can be liberated.
Fundamental Safety Precautions
1. Avoid Inhalation
Under no circumstances should one inhale the dust or gas. When there is a risk of inhaling cyanide dust, such as when handling cyanide containers or during the mixing of cyanide substances, it is imperative to wear an approved dust mask.
2. Prevent Skin Contact
Cyanide should be kept away from the skin at all times. It must never come into contact with open wounds or abraded skin. When handling solid cyanide, wear protective gloves. For handling cyanide solutions, rubber gloves are recommended. After handling cyanide, both hands and gloves should be thoroughly washed with tap water.
3. Protect the Eyes
Take measures to prevent cyanide from entering the eyes. When working with cyanide solutions or in situations where there is a risk of splashing, wear approved chemical splash goggles.
4. Manage Spills Promptly
In the event of any cyanide spill, immediately sweep it onto a shovel and place it in an appropriate container. Swift action is crucial to minimize exposure and potential hazards.
5. Prevent Reactive Substance Contact
Implement all possible precautions to prevent acids or weak bases from coming into contact with sodium cyanide. It is advisable not to store acids or weak bases in the vicinity of sodium cyanide.
6. Maintain a Safe Environment
Food, beverages, and smoking materials should never be stored, handled, or consumed in areas where cyanide is being used, processed, or stored. This helps to prevent accidental ingestion or inhalation of cyanide residues.
7. Proper Storage
During storage, keep sodium cyanide dry and ensure that the containers are tightly closed. Store sodium cyanide in a dry, well - ventilated area to prevent the release of toxic gases and maintain the integrity of the chemical.
By following these safety precautions rigorously, the risks associated with handling sodium cyanide can be significantly mitigated, ensuring the safety of personnel and the surrounding environment.
- Random Content
- Hot content
- Hot review content
- Industrial concentrated nitric acid 55%-68%
- Sodium Isobutyl Xanthate SIBX 90%
- Booster(Detonating insensitive explosives)
- Shock Tube Detonator
- Ferrous Sulfate Industrial Grade 90%
- Dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid
- Sodium Metasilicate Pentahydrate
- 1Discounted Sodium Cyanide (CAS: 143-33-9) for Mining - High Quality & Competitive Pricing
- 2Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 3Sodium Cyanide 98%+ CAS 143-33-9
- 4China's New Regulations on Sodium Cyanide Exports and Guidance for International Buyers
- 5Anhydrous Oxalic acid 99.6% Industrial Grade
- 6Oxalic acid for mining 99.6%
- 7Reagent Grade/Industrial Grade Hydrochloric Acid min.31%
- 1Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 2High Quality 99% Purity of Cyanuric chloride ISO 9001:2005 REACH Verified Producer
- 3 High-Quality Sodium Cyanide for Leaching
- 4Powdery emulsion explosive
- 5Industry Grade Electron grade 98% Sulfuric Acid H2SO4 Sulphuric Acid Battery Acid Industrial Sulfuric Acid
- 6Colloidal emulsion explosive
- 7sodium hydrosulfide 70% flakes used Mining Industry










Online message consultation
Add comment: